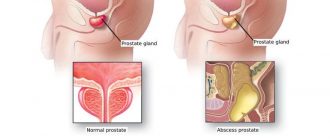
Blood in the urine due to prostatitis (hematuria) or other diseases of the genitourinary system, including the kidneys, occurs due to inflammatory processes, tumors and injuries. These pathologies can damage blood vessels and capillaries, resulting in this symptom. To eliminate it, at the first manifestation it is necessary to contact a urologist and undergo a comprehensive diagnosis to identify the cause. Depending on it, treatment will be prescribed.
Causes
Blood in the urine with prostatitis can be for several reasons:
- In the acute form or exacerbation of the chronic form of inflammation, vascular permeability increases, which can cause blood clots to enter the urinary canal.
- Hematuria with prostate adenoma in combination with chronic inflammation is also possible.
- During the oncological process as a result of gland growth and destruction of blood vessels.
- With calculous prostatitis or the occurrence of calcifications, mechanical damage to the vessels occurs, which can cause bleeding from the urethra.
- When an abscess (purulent inflammation) occurs, the walls of the blood vessels may become damaged and allow some blood to leak into the urethra.
- Urine with blood in prostatitis is observed after operations, including installation and removal of a catheter. In this case, this is considered a normal phenomenon that goes away on its own within a few days. If this does not happen, you must inform your doctor.
- Hematuria with prostatitis also occurs due to the spread of inflammation to nearby tissues and organs - the bladder and urinary canal.
- Due to taking certain anticoagulants or other drugs that reduce blood clotting.
- Changes in urine color may occur after eating certain foods that contain dyes (such as beets).
In addition to evidence of diseases of the pelvic organs, hematuria can signal inflammation in the kidneys. With pyelonephritis and nephritis, small capillaries are destroyed, but often blood enters the urine in clots, most often at the end of urination.
In addition to these diseases, less common causes may be kidney injuries, metabolic disorders, and liver pathologies. To establish the exact cause and eliminate the symptom, it is necessary to undergo a thorough diagnosis.
What to do if detected
Bloody discharge due to prostate adenoma or prostatitis is eliminated only together with the cause of its appearance, i.e. the disease itself. When this symptom first appears, you should consult a doctor. After collecting an anamnesis and an initial examination, blood and urine tests will be prescribed. Depending on their results, the patient will be referred for further studies, which may include:
- Palpation of the prostate gland.
- Collection of prostate secretions.
- Ultrasound of the kidneys and pelvic organs.
- Uroflowmetry (urination study).
Completing these procedures with high accuracy will allow you to determine the disease.
Treatment
Treatment for the appearance of blood in the urine due to prostate adenoma, prostatitis or nephritis is carried out after accurate identification of the disease. Depending on the causes of the pathology, medications, physiological procedures and folk remedies are prescribed. A therapeutic diet and preventive measures may also be prescribed.
The basis of therapy will be medications that eliminate the cause of the disease. In case of bacterial origin, the type of bacteria is identified and a study is carried out on the effectiveness of their elimination with various antibiotics. The most effective ones will be prescribed as therapy. Symptomatic medications are also prescribed to eliminate other manifestations of pathology. Most often these are drugs from the group of alpha-blockers, analgesics, antispasmodics and anti-inflammatory drugs.
In the most severe situations and cases where therapy is ineffective, surgery is prescribed, which involves complete or partial removal of the diseased organ.
Prevention
There are no specific recommendations to prevent this phenomenon. You should adhere to general preventive recommendations for prostate and kidney diseases:
- Have a regular sexual partner, use protective equipment.
- To live an active lifestyle.
- Eat right; plant foods should predominate in your diet.
- Drink enough water.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Avoid injury and hypothermia.