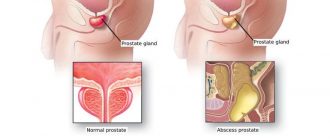
A burning sensation in the prostate is not a disease, but only a symptom that the functioning of the male genitourinary system is impaired. The reasons for its appearance can be many pathologies of infectious or non-bacterial origin. For therapy, it is necessary to undergo a thorough diagnosis and accurately determine the cause of the disease.
Causes
A burning sensation in the prostate area may be the first signal of the presence of a disease of the pelvic organs. Most often, the symptom occurs after urination or ejaculation, in the morning or evening.
The prostate itches in men because an infection occurs in the organs of the genitourinary system. The most common diagnosis in this case is prostatitis. But the causes of inflammation can also be non-infectious in nature, but arise as a result of stagnation. In such cases, a burning sensation in the prostate can occur when sitting, lying down or in another state of rest and has no connection with urination and sexual intercourse.
In men with prostatitis, a burning sensation in the urethra can occur together with itching in the anus, pain in the groin, buttocks and lower back. Other characteristic signs of pathologies of the pelvic organs also appear. However, almost all diseases of the genitourinary system cause similar symptoms, so it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis based only on them - a comprehensive examination is required.
The infectious origin of itching and burning in the anus or prostate gland is most often caused by the following bacteria:
- coli;
- klebsiella;
- gonococcus;
- trichomonas;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- chlamydia;
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa;
- proteas;
- ureaplasma;
- enerococci;
- Candida fungi;
- mycoplasmas.
Most of them enter the body from the outside (often sexually), through unprotected sexual intercourse. However, some live inside the body (in the intestines) and are opportunistic, i.e. they can live even in a healthy body without causing any consequences, but, when the immune system is weakened, they begin to actively multiply and enter adjacent tissues with the bloodstream, where they cause inflammation.
A burning sensation in the prostate or anus can also be caused by non-infectious pathologies:
- benign hyperplasia (adenoma);
- malignant neoplasm in the prostate gland (cancer);
- calcifications (stones) in the prostate or bladder;
- haemorrhoids;
- allergic reaction to medications (especially those administered rectally);
- parasites in the intestines;
- dysbacteriosis;
- violation of hygiene.
Factors that provoke a burning sensation after urination include:
- unsafe sexual acts, frequent changes of partner;
- a long period of abstinence or, on the contrary, excessively intense sexual intercourse;
- frequent local or general hypothermia or overheating;
- frequent consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- smoking;
- poor nutrition;
- the appearance of microtraumas in the perineal area as a result of physical activity (sports, especially horseback riding or cycling, lifting weights, long-term driving).
Diagnostics
Taking into account the fact that a burning sensation in the head can occur with a wide range of diseases, the urologist will first conduct an anamnesis, the purpose of which will be to find out what other symptoms are observed. A visual examination of the external genitalia and palpation of the prostate will also be performed. This will provide preliminary information, but an accurate diagnosis of the cause of a burning sensation in the prostate area can only be provided by instrumental and laboratory tests:
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Stool analysis (allows you to confirm the presence of parasites in the intestines or dysbacteriosis).
- Biochemistry of blood.
- Ultrasound or TRUS of the pelvic organs (or CT or MRI, if possible).
- Smear of urethral contents.
- Microscopic examination of prostate secretion.
- Bacterial culture of prostate secretion (allows not only to identify the causative agent of infection, if any, but also to check the effectiveness of treatment with various antibiotics).
- PSA blood test.
- Uroflowmetry (study of the urination process).
Examinations are not prescribed all at once, but begin with general ones, gradually narrowing the range of possible diseases.
Treatment
It is possible to remove a burning sensation due to prostatitis or other pathology of the genitourinary system only by eliminating the cause of its occurrence - that is, the disease itself. In the case of an infectious nature of its origin, antibiotics will become the basis of therapy. In addition to them, other drugs from the following groups are prescribed:
- Immunomodulators.
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers.
Treatment of prostate burning in the case of non-infectious origin involves taking:
- Anti-inflammatory.
- Medicines that stimulate blood circulation.
- Muscle relaxants.
Medicines to relieve unpleasant symptoms (painkillers) and hepatoprotectors may also be prescribed, because taking antibiotics and a large number of other drugs has a negative effect on the liver. Vitamin and mineral complexes may also be prescribed to improve the functioning of the immune system.
In cases of advanced disease or failure of conservative treatment, surgical intervention is prescribed. It involves the removal of part of the affected organ and requires preliminary preparation and postoperative rehabilitation. Most often, surgical operations are performed in cases where the disease threatens the patient's life.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of infections and congestion in the male genital organs, you should follow simple recommendations:
- observe the rules of hygiene;
- have a regular sexual partner. Sex should be regular, not too frequent, but without periods of abstinence;
- sexual intercourse must be safe;
- you should lead an active lifestyle, but observing reasonable restrictions on exercise;
- proper nutrition promotes the functioning of the immune system and prevents congestion;
- you need to undergo regular medical examinations, including with a urologist (recommended once a year).